Tutorial
Introduction
This is a port of a well known tutorial for the JuliaDB package. This tutorial is available as a Jupyter notebook here.
Getting the data
The flights dataset for the tutorial is here. Alternatively, run the following in Julia:
download("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/piever/JuliaDBTutorial/master/hflights.csv")Loading the data
Loading a csv file is straightforward with JuliaDB:
using JuliaDB
flights = loadtable("hflights.csv")Of course, replace the path with the location of the dataset you have just downloaded.
Filtering the data
In order to select only rows matching certain criteria, use the filter function:
filter(i -> (i.Month == 1) && (i.DayofMonth == 1), flights)To test if one of two conditions is verified:
filter(i -> (i.UniqueCarrier == "AA") || (i.UniqueCarrier == "UA"), flights)
# in this case, you can simply test whether the `UniqueCarrier` is in a given list:
filter(i -> i.UniqueCarrier in ["AA", "UA"], flights)Select: pick columns by name
You can use the select function to select a subset of columns:
select(flights, (:DepTime, :ArrTime, :FlightNum))Table with 227496 rows, 3 columns:
DepTime ArrTime FlightNum
───────────────────────────
1400 1500 428
1401 1501 428
1352 1502 428
1403 1513 428
1405 1507 428
1359 1503 428
1359 1509 428
1355 1454 428
1443 1554 428
1443 1553 428
1429 1539 428
1419 1515 428
⋮
1939 2119 124
556 745 280
1026 1208 782
1611 1746 1050
758 1051 201
1307 1600 471
1818 2111 1191
2047 2334 1674
912 1031 127
656 812 621
1600 1713 1597Let's select all columns between :Year and :Month as well as all columns containing "Taxi" or "Delay" in their name. Between selects columns between two specified extremes, passing a function filters column names by that function and All takes the union of all selectors (or all columns, if no selector is specified).
select(flights, All(Between(:Year, :DayofMonth), i -> occursin("Taxi", string(i)), i -> occursin("Delay", string(i))))Table with 227496 rows, 7 columns:
Year Month DayofMonth TaxiIn TaxiOut ArrDelay DepDelay
────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
2011 1 1 7 13 -10 0
2011 1 2 6 9 -9 1
2011 1 3 5 17 -8 -8
2011 1 4 9 22 3 3
2011 1 5 9 9 -3 5
2011 1 6 6 13 -7 -1
2011 1 7 12 15 -1 -1
2011 1 8 7 12 -16 -5
2011 1 9 8 22 44 43
2011 1 10 6 19 43 43
2011 1 11 8 20 29 29
2011 1 12 4 11 5 19
⋮
2011 12 6 4 15 14 39
2011 12 6 13 9 -10 -4
2011 12 6 4 12 -12 1
2011 12 6 3 9 -9 16
2011 12 6 3 10 -4 -2
2011 12 6 5 10 0 7
2011 12 6 5 11 -9 8
2011 12 6 4 9 4 7
2011 12 6 4 14 -4 -3
2011 12 6 3 9 -13 -4
2011 12 6 3 11 -12 0The same could be achieved more concisely using regular expressions:
select(flights, All(Between(:Year, :DayofMonth), r"Taxi|Delay"))Applying several operations
If one wants to apply several operations one after the other, there are two main approaches:
- nesting
- piping
Let's assume we want to select UniqueCarrier and DepDelay columns and filter for delays over 60 minutes. Since the DepDelay column has missing data, we also need to filter out missing values via !ismissing. The nesting approach would be:
filter(i -> !ismissing(i.DepDelay > 60), select(flights, (:UniqueCarrier, :DepDelay)))Table with 224591 rows, 2 columns:
UniqueCarrier DepDelay
───────────────────────
"AA" 0
"AA" 1
"AA" -8
"AA" 3
"AA" 5
"AA" -1
"AA" -1
"AA" -5
"AA" 43
"AA" 43
⋮
"WN" 1
"WN" 16
"WN" -2
"WN" 7
"WN" 8
"WN" 7
"WN" -3
"WN" -4
"WN" 0For piping, we'll use the excellent Lazy package.
import Lazy
Lazy.@as x flights begin
select(x, (:UniqueCarrier, :DepDelay))
filter(i -> !ismissing(i.DepDelay > 60), x)
endTable with 224591 rows, 2 columns:
UniqueCarrier DepDelay
───────────────────────
"AA" 0
"AA" 1
"AA" -8
"AA" 3
"AA" 5
"AA" -1
"AA" -1
"AA" -5
"AA" 43
"AA" 43
⋮
"WN" 1
"WN" 16
"WN" -2
"WN" 7
"WN" 8
"WN" 7
"WN" -3
"WN" -4
"WN" 0where the variable x denotes our data at each stage. At the beginning it is flights, then it only has the two relevant columns and, at the last step, it is filtered.
Reorder rows
Select UniqueCarrier and DepDelay columns and sort by DepDelay:
sort(flights, :DepDelay, select = (:UniqueCarrier, :DepDelay))Table with 227496 rows, 2 columns:
UniqueCarrier DepDelay
───────────────────────
"OO" -33
"MQ" -23
"XE" -19
"XE" -19
"CO" -18
"EV" -18
"XE" -17
"CO" -17
"XE" -17
"MQ" -17
"XE" -17
"DL" -17
⋮
"US" missing
"US" missing
"US" missing
"WN" missing
"WN" missing
"WN" missing
"WN" missing
"WN" missing
"WN" missing
"WN" missing
"WN" missingor, in reverse order:
sort(flights, :DepDelay, select = (:UniqueCarrier, :DepDelay), rev = true)Apply a function row by row
To apply a function row by row, use map: the first argument is the anonymous function, the second is the dataset.
speed = map(i -> i.Distance / i.AirTime * 60, flights)227496-element Array{Union{Missing, Float64},1}:
336.0
298.6666666666667
280.0
344.61538461538464
305.45454545454544
298.6666666666667
312.55813953488376
336.0
327.8048780487805
298.6666666666667
320.0
⋮
473.7931034482758
479.30232558139534
496.6265060240964
468.59999999999997
478.1632653061224
483.0927835051546
498.5106382978723
445.57377049180326
424.6875
460.6779661016949Add new variables
Use the pushcol function to add a column to an existing dataset:
pushcol(flights, :Speed, speed)If you need to add the new column to the existing dataset:
flights = pushcol(flights, :Speed, speed)Reduce variables to values
To get the average delay, we first filter away datapoints where ArrDelay is missing, then group by :Dest, select :ArrDelay and compute the mean:
using Statistics
groupby(mean ∘ skipmissing, flights, :Dest, select = :ArrDelay)Table with 116 rows, 2 columns:
Dest avg_delay
────────────────
"ABQ" 7.22626
"AEX" 5.83944
"AGS" 4.0
"AMA" 6.8401
"ANC" 26.0806
"ASE" 6.79464
"ATL" 8.23325
"AUS" 7.44872
"AVL" 9.97399
"BFL" -13.1988
"BHM" 8.69583
"BKG" -16.2336
⋮
"SJU" 11.5464
"SLC" 1.10485
"SMF" 4.66271
"SNA" 0.35801
"STL" 7.45488
"TPA" 4.88038
"TUL" 6.35171
"TUS" 7.80168
"TYS" 11.3659
"VPS" 12.4572
"XNA" 6.89628Performance tip
If you'll group often by the same variable, you can sort your data by that variable at once to optimize future computations.
sortedflights = reindex(flights, :Dest)Table with 227496 rows, 22 columns:
Columns:
# colname type
────────────────────────────────────────────────────
1 Dest String
2 Year Int64
3 Month Int64
4 DayofMonth Int64
5 DayOfWeek Int64
6 DepTime DataValues.DataValue{Int64}
7 ArrTime DataValues.DataValue{Int64}
8 UniqueCarrier String
9 FlightNum Int64
10 TailNum String
11 ActualElapsedTime DataValues.DataValue{Int64}
12 AirTime DataValues.DataValue{Int64}
13 ArrDelay DataValues.DataValue{Int64}
14 DepDelay DataValues.DataValue{Int64}
15 Origin String
16 Distance Int64
17 TaxiIn DataValues.DataValue{Int64}
18 TaxiOut DataValues.DataValue{Int64}
19 Cancelled Int64
20 CancellationCode String
21 Diverted Int64
22 Speed DataValues.DataValue{Float64}using BenchmarkTools
println("Presorted timing:")
@benchmark groupby(mean ∘ skipmissing, sortedflights, select = :ArrDelay)Presorted timing:
BenchmarkTools.Trial:
memory estimate: 31.23 MiB
allocs estimate: 1588558
--------------
minimum time: 39.565 ms (8.03% GC)
median time: 44.401 ms (9.83% GC)
mean time: 44.990 ms (10.36% GC)
maximum time: 57.016 ms (15.96% GC)
--------------
samples: 112
evals/sample: 1println("Non presorted timing:")
@benchmark groupby(mean ∘ skipmissing, flights, select = :ArrDelay)Non presorted timing:
BenchmarkTools.Trial:
memory estimate: 1.81 KiB
allocs estimate: 30
--------------
minimum time: 195.095 μs (0.00% GC)
median time: 212.309 μs (0.00% GC)
mean time: 230.878 μs (0.20% GC)
maximum time: 4.859 ms (95.04% GC)
--------------
samples: 10000
evals/sample: 1Using summarize, we can summarize several columns at the same time:
summarize(mean ∘ skipmissing, flights, :Dest, select = (:Cancelled, :Diverted))
# For each carrier, calculate the minimum and maximum arrival and departure delays:
cols = Tuple(findall(i -> occursin("Delay", string(i)), colnames(flights)))
summarize((min = minimum∘skipmissing, max = maximum∘skipmissing), flights, :UniqueCarrier, select = cols)Table with 15 rows, 5 columns:
UniqueCarrier ArrDelay_min DepDelay_min ArrDelay_max DepDelay_max
─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
"AA" -39 -15 978 970
"AS" -43 -15 183 172
"B6" -44 -14 335 310
"CO" -55 -18 957 981
"DL" -32 -17 701 730
"EV" -40 -18 469 479
"F9" -24 -15 277 275
"FL" -30 -14 500 507
"MQ" -38 -23 918 931
"OO" -57 -33 380 360
"UA" -47 -11 861 869
"US" -42 -17 433 425
"WN" -44 -10 499 548
"XE" -70 -19 634 628
"YV" -32 -11 72 54For each day of the year, count the total number of flights and sort in descending order:
Lazy.@as x flights begin
groupby(length, x, :DayofMonth)
sort(x, :length, rev = true)
endTable with 31 rows, 2 columns:
DayofMonth length
──────────────────
28 7777
27 7717
21 7698
14 7694
7 7621
18 7613
6 7606
20 7599
11 7578
13 7546
10 7541
17 7537
⋮
25 7406
16 7389
8 7366
12 7301
4 7297
19 7295
24 7234
5 7223
30 6728
29 6697
31 4339For each destination, count the total number of flights and the number of distinct planes that flew there
groupby((flight_count = length, plane_count = length∘union), flights, :Dest, select = :TailNum)Table with 116 rows, 3 columns:
Dest flight_count plane_count
────────────────────────────────
"ABQ" 2812 716
"AEX" 724 215
"AGS" 1 1
"AMA" 1297 158
"ANC" 125 38
"ASE" 125 60
"ATL" 7886 983
"AUS" 5022 1015
"AVL" 350 142
"BFL" 504 70
"BHM" 2736 616
"BKG" 110 63
⋮
"SJU" 391 115
"SLC" 2033 368
"SMF" 1014 184
"SNA" 1661 67
"STL" 2509 788
"TPA" 3085 697
"TUL" 2924 771
"TUS" 1565 226
"TYS" 1210 227
"VPS" 880 224
"XNA" 1172 177Window functions
In the previous section, we always applied functions that reduced a table or vector to a single value. Window functions instead take a vector and return a vector of the same length, and can also be used to manipulate data. For example we can rank, within each UniqueCarrier, how much delay a given flight had and figure out the day and month with the two greatest delays:
using StatsBase
fc = dropmissing(flights, :DepDelay)
gfc = groupby(fc, :UniqueCarrier, select = (:Month, :DayofMonth, :DepDelay), flatten = true) do dd
rks = ordinalrank(column(dd, :DepDelay), rev = true)
sort(dd[rks .<= 2], by = i -> i.DepDelay, rev = true)
endTable with 30 rows, 4 columns:
UniqueCarrier Month DayofMonth DepDelay
──────────────────────────────────────────
"AA" 12 12 970
"AA" 11 19 677
"AS" 2 28 172
"AS" 7 6 138
"B6" 10 29 310
"B6" 8 19 283
"CO" 8 1 981
"CO" 1 20 780
"DL" 10 25 730
"DL" 4 5 497
"EV" 6 25 479
"EV" 1 5 465
⋮
"OO" 4 4 343
"UA" 6 21 869
"UA" 9 18 588
"US" 4 19 425
"US" 8 26 277
"WN" 4 8 548
"WN" 9 29 503
"XE" 12 29 628
"XE" 12 29 511
"YV" 4 22 54
"YV" 4 30 46Though in this case, it would have been simpler to use Julia partial sorting:
groupby(fc, :UniqueCarrier, select = (:Month, :DayofMonth, :DepDelay), flatten = true) do dd
partialsort(dd, 1:2, by = i -> i.DepDelay, rev = true)
endTable with 30 rows, 4 columns:
UniqueCarrier Month DayofMonth DepDelay
──────────────────────────────────────────
"AA" 12 12 970
"AA" 11 19 677
"AS" 2 28 172
"AS" 7 6 138
"B6" 10 29 310
"B6" 8 19 283
"CO" 8 1 981
"CO" 1 20 780
"DL" 10 25 730
"DL" 4 5 497
"EV" 6 25 479
"EV" 1 5 465
⋮
"OO" 4 4 343
"UA" 6 21 869
"UA" 9 18 588
"US" 4 19 425
"US" 8 26 277
"WN" 4 8 548
"WN" 9 29 503
"XE" 12 29 628
"XE" 12 29 511
"YV" 4 22 54
"YV" 4 30 46For each month, calculate the number of flights and the change from the previous month
using ShiftedArrays
y = groupby(length, flights, :Month)
lengths = columns(y, :length)
pushcol(y, :change, lengths .- lag(lengths))Table with 12 rows, 3 columns:
Month length change
─────────────────────
1 18910 missing
2 17128 -1782
3 19470 2342
4 18593 -877
5 19172 579
6 19600 428
7 20548 948
8 20176 -372
9 18065 -2111
10 18696 631
11 18021 -675
12 19117 1096Visualizing your data
The StatsPlots and GroupedErrors package as well as native plotting recipes from JuliaDB using OnlineStats make a rich set of visualizations possible with an intuitive syntax.
Use the @df macro to be able to refer to columns simply by their name. You can work with these symobls as if they are regular vectors. Here for example, we split data according to whether the distance is smaller or bigger than 1000.
using StatsPlots
gr(fmt = :png) # choose the fast GR backend and set format to png: svg would probably crash with so many points
@df flights scatter(:DepDelay, :ArrDelay, group = :Distance .> 1000, layout = 2, legend = :topleft)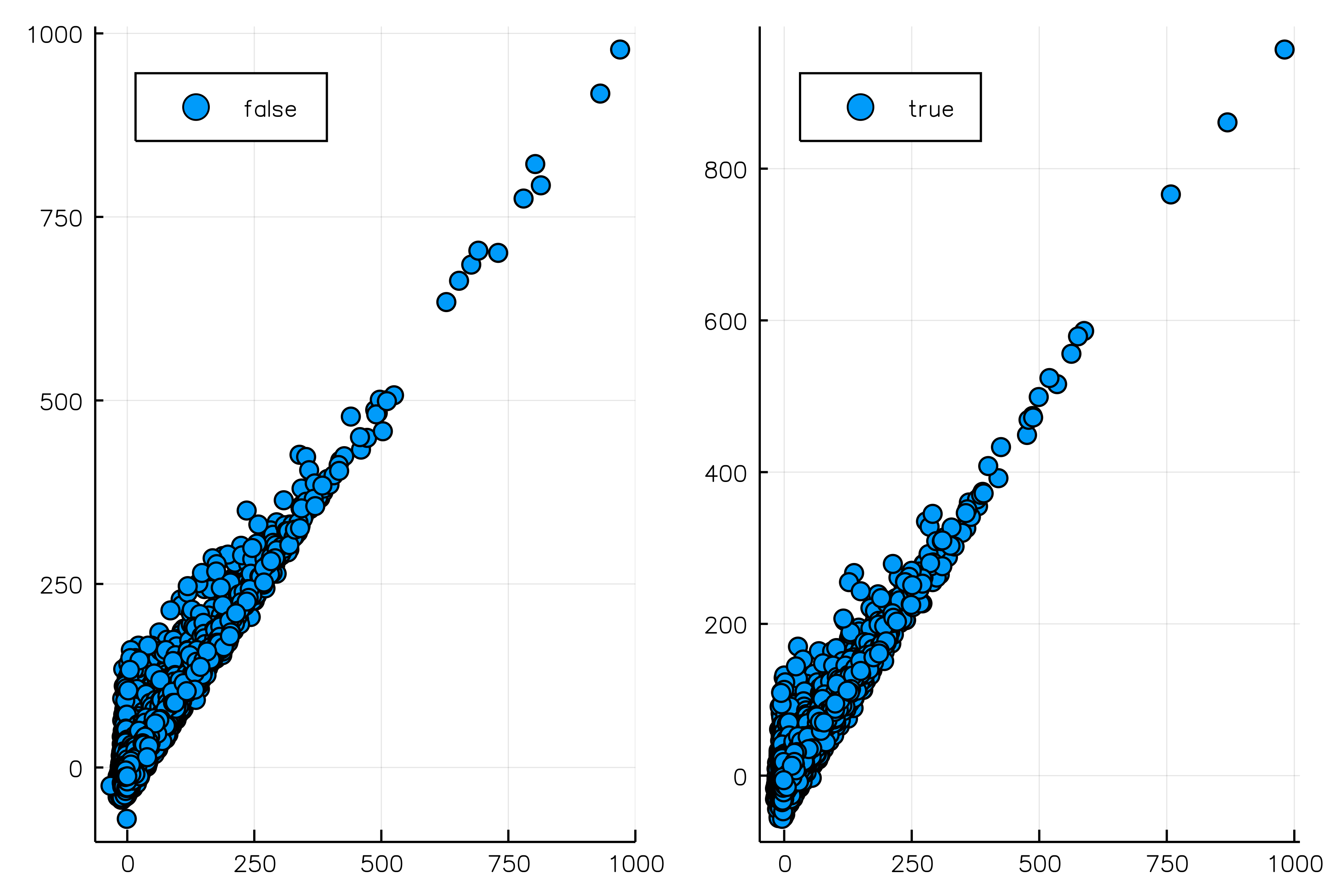
Online statistics
For large datasets, summary statistics can be computed using efficient online algorithms implemnted in OnlineStats. Here we will use an online algorithm to compute the mean traveled distance split across month of the year.
using OnlineStats
grpred = groupreduce(Mean(), flights, :Month; select = :Distance)Table with 12 rows, 2 columns:
Month Mean
────────────────────────────────────
1 Mean: n=18910 | value=760.804
2 Mean: n=17128 | value=763.909
3 Mean: n=19470 | value=782.788
4 Mean: n=18593 | value=783.845
5 Mean: n=19172 | value=789.66
6 Mean: n=19600 | value=797.869
7 Mean: n=20548 | value=798.52
8 Mean: n=20176 | value=793.727
9 Mean: n=18065 | value=790.444
10 Mean: n=18696 | value=788.256
11 Mean: n=18021 | value=790.691
12 Mean: n=19117 | value=809.024Extract the values of the OnlineStat objects with the value function.
select(grpred, (:Month, :Mean => value))Table with 12 rows, 2 columns:
Month Mean
──────────────
1 760.804
2 763.909
3 782.788
4 783.845
5 789.66
6 797.869
7 798.52
8 793.727
9 790.444
10 788.256
11 790.691
12 809.024Interfacing with online datasets
JuliaDB can also smoothly interface online datasets using packages from the JuliaDatabases organization. Here's how it would work with a MySQL dataset:
using MySQL, JuliaDBconn = MySQL.connect(host::String, user::String, passwd::String; db::String = "") # edit as needed for your dataset
MySQL.query(conn, "SELECT Name, Salary FROM Employee;") |> table # execute the query and collect as a table
MySQL.disconnect(conn)